Blog
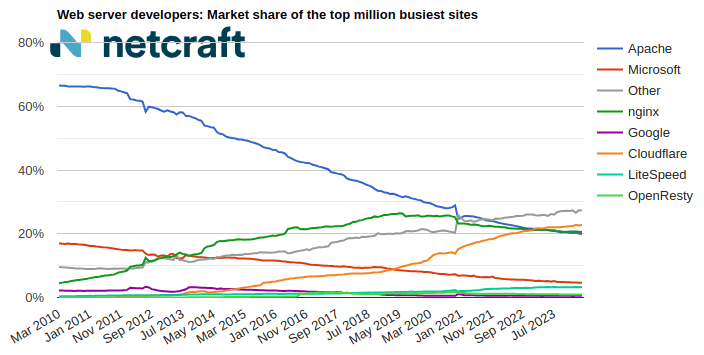
April 2024 Web Server Survey
In the April 2024 survey we received responses from 1,092,963,063 sites across 267,934,761 domains and 12,872,291 web-facing computers. This reflects ... Read More
Learn More
Blog
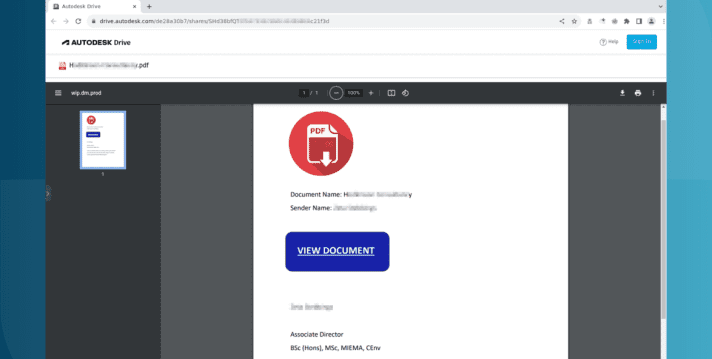
Autodesk hosting PDF files used in Microsoft phishing attacks
Autodesk is hosting malicious PDF files that lead phishing attack victims to have their Microsoft login credentials stolen. The elaborate ... Read More
Learn More
Blog
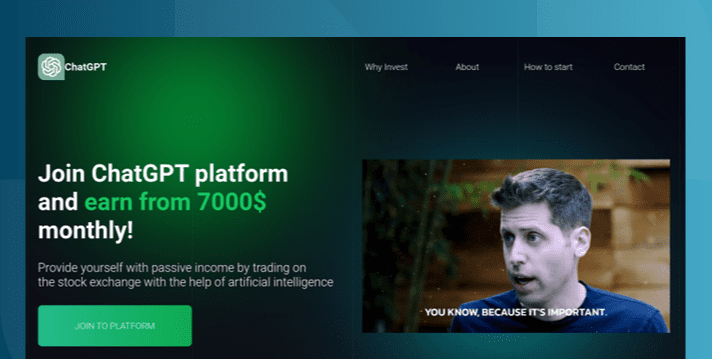
The AI Gold Rush: ChatGPT and OpenAI targeted in AI-themed investment scams
Investment scams and AI – a match made in heaven? Online investment scams are a big money spinner for ... Read More
Learn More

Blog
UN? FBI? World Bank? Deepfake police chief used for compensation scam video
Advance fee fraud campaigns are using generative AI in both text and video to speed up responses, evade filters, and ... Read More
Learn More
Blog
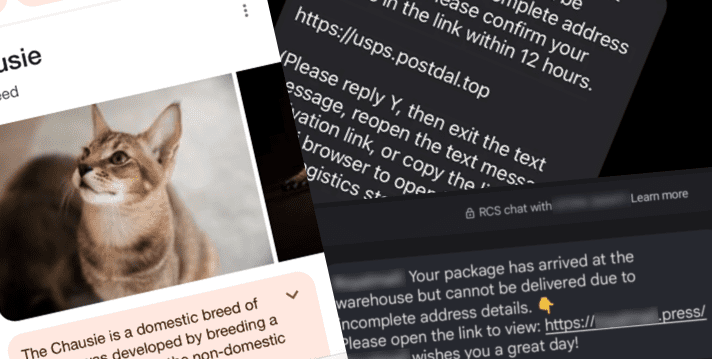
Out of the shadows – ’darcula’ iMessage and RCS smishing attacks target USPS and global postal services
Chinese-language Phishing-as-a-Service platform ‘darcula’ targets organizations in 100+ countries with sophisticated techniques using more than 20,000 phishing domains ‘darcula’ [sic] ... Read More
Learn More
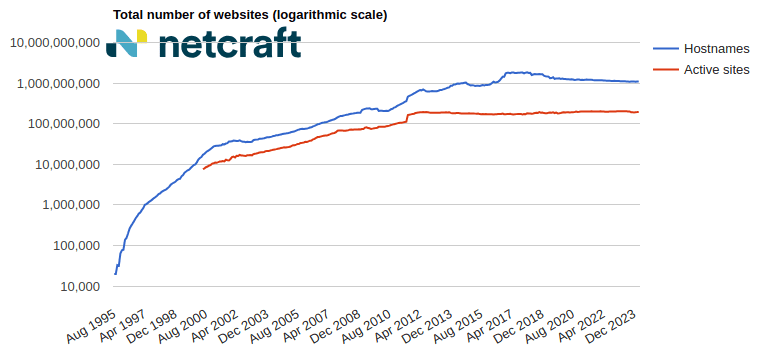
Blog
March 2024 Web Server Survey
In the March 2024 survey we received responses from 1,090,117,902 sites across 271,804,260 domains and 12,627,575 web-facing computers. This reflects ... Read More
Learn More
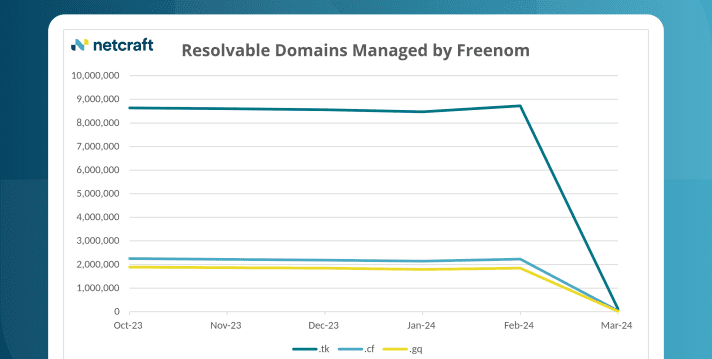
Blog
Cloudflare loses 22% of its domains in Freenom .tk shutdown
A staggering 12.6 million domains on TLDs controlled by Freenom (.tk, .cf and .gq) have been shut down and no ... Read More
Learn More

Blog
Online investment scams: Inside a fake trading platform
Online investment scams are a global, growing, and uniquely pernicious threat. In newly released data, the Federal Trade Commission attributed ... Read More
Learn More
